
If
the surface is smooth and shiny, the light will reflect at the same
angle at which it hits the surface. This is called regular reflection
and produces good images. But for rough surfaces, the rays incident
at slightly different points on the surface are reflected in
completely different directions, because the normal to a rough
surface varies in direction very strongly from point to point on the
surface. This type of reflection is called diffuse reflection and
this enable us to see non-shiny objects.
Laws
of Reflections
The
laws of reflections governs the reflection of light rays off smooth
conducting surfaces and there are three laws for the reflection of
light. They are :-
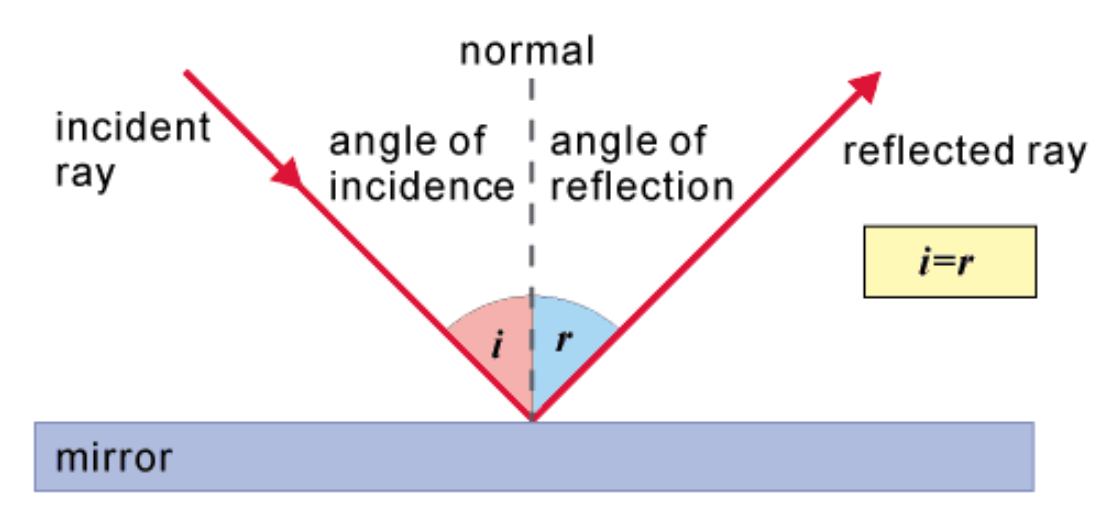
>>>Plane Of Incidence
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence are all lie on the same plane; while the incident ray is the beam of light that initially strikes the mirror and the reflected ray is the beam of light that bounces off the mirror after striking the mirror.
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence are all lie on the same plane; while the incident ray is the beam of light that initially strikes the mirror and the reflected ray is the beam of light that bounces off the mirror after striking the mirror.
>>>
The reflected ray and the incident ray are on the opposite sides of
the normal.
>>>
The angle of incidence (i) is equal to the angle of reflection (r)
that means the angle which the incident ray makes to the normal in
equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal
Comments
Post a Comment