
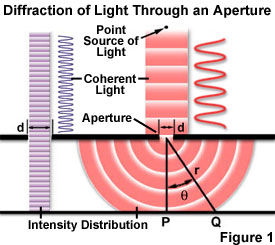
Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit. It is defined as the bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/ aperture. In case of light, the diffraction is the slight bending of light as it passes around the edge of an object. The amount of bending depends on the relative size of the wavelength of light to the size of the opening. If the opening is much larger than than the light's wavelength, the bending will be unnoticeable. But if the opening and the light's wavelength are in closer in size or equal, the amount of bending will be noticeable and can be seen with our naked eye.
 |
| Francesco Grimaldi |

In
atmosphere, diffracted light is actually bent around the atmospheric
particles like tiny water droplets found in clouds. Diffracted light
can produce fringes of light, dark or coloured bands. An optical
effect that results from the diffraction of light is the silver
lining found around the edges of clouds. An Italian natural
philosopher Francesco Grimaldi discovered and coined the term
'Diffraction' in 1660. Optical effects resulting from diffraction are
produced through the interference of light waves.
Comments
Post a Comment